Tag: study
-

Newly identified chemical in drinking water could be toxic: study
The Summary A newly identified chemical byproduct may be present in drinking water in about a third of U.S. homes, a study found. Scientists do not yet know whether the byproduct is dangerous. But some are worried that it could have toxic properties because of similarities to other chemicals of concern. About a third of…
-

In a polarized nation, local governments are oases of compromise and community, study finds
Local governments are uniquely able to combat growing national polarization, according to a new study out Wednesday from the nonprofit research organization CivicPulse and the Carnegie Corporation of New York. The study, which features quantitative and qualitative conclusions following interviews with more than 1,400 local elected policymakers and local civil service leaders, found that 87%…
-

Columbus was a Sephardic Jew from Western Europe, study finds
The 15th-century explorer Christopher Columbus was a Sephardic Jew from Western Europe, Spanish scientists said on Saturday, after using DNA analysis to tackle a centuries-old mystery. Several countries have argued over the origins and the final burial place of the divisive figure who led Spanish-funded expeditions from the 1490s onward, opening the way for the…
-

Arm position during blood pressure check may result in wrong hypertension diagnosis, study finds
Blood pressure readings may not be accurate unless a person’s arm is positioned correctly, a new study suggests. A comparison of blood pressure readings taken while people held their arms three different ways — leaning on a desk, resting on the lap or hanging by the side of the body — showed certain positions could…
-

Do we still need fluoride in drinking water? The benefits may be waning, study suggests
The widespread use of toothpaste and mouthwashes with added fluoride in recent decades appears to have diminished the known public health benefits of water fluoridation, a new study suggests. But it would be a mistake for municipalities to interpret the findings as a reason to pull back on adding the cavity-fighting mineral to their water…
-
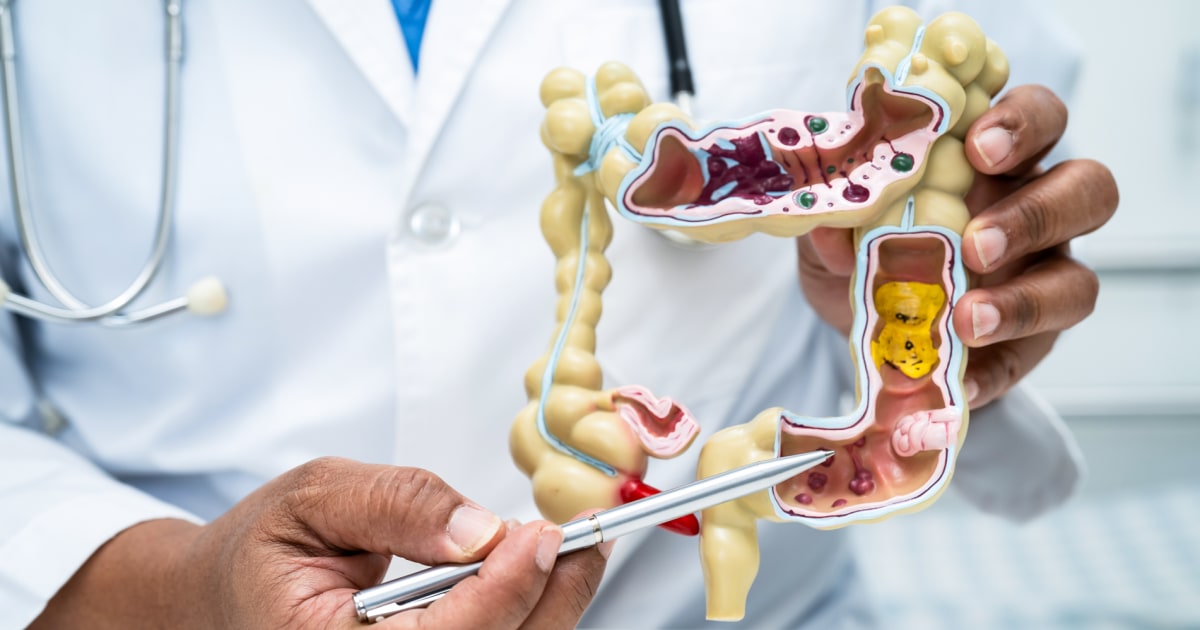
More younger people are getting colonoscopies, a new study suggests
After the recommended age to start screening for colorectal cancer was lowered to 45, there was a small but significant increase in screenings among younger people, according to a study published in the journal JAMA Network Open. The lower screening age was put into place in 2021 by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which…
-

Study establishes first causal link between anti-trans laws and suicide attempts
State laws targeting transgender people made trans and nonbinary young people more likely to attempt suicide in the past year, according to a first-of-its-kind study. The research, published last week in the journal Nature Human Behavior and conducted by the Trevor Project, an LGBTQ youth suicide prevention and crisis intervention organization, is the first to…
-
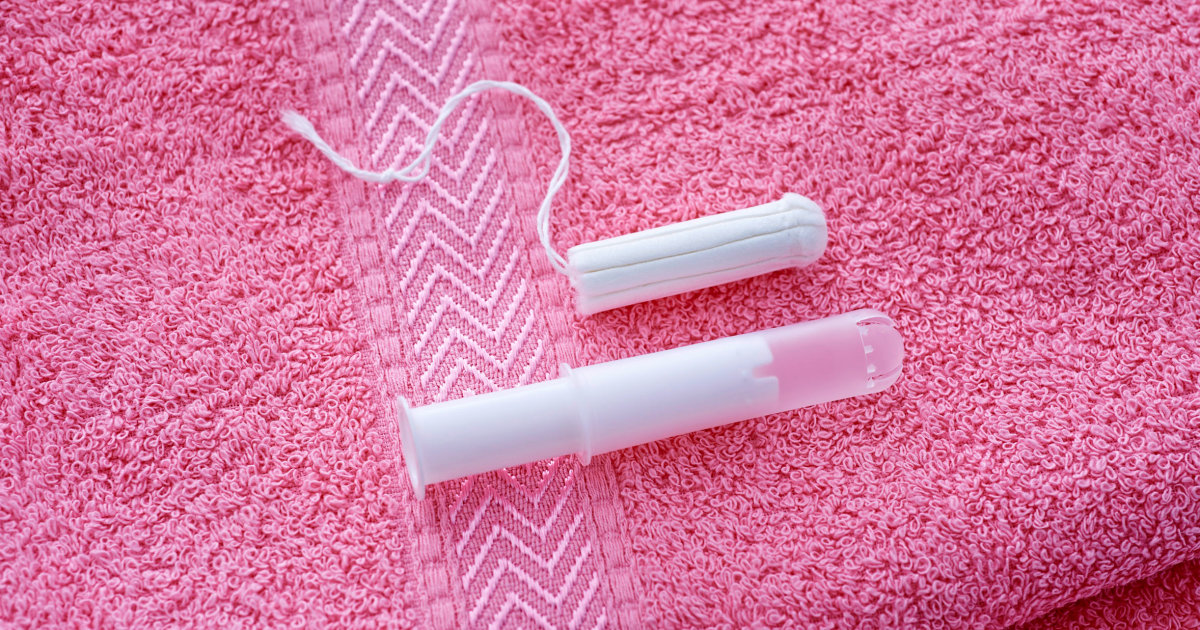

1 in 3 teens can’t get tampons or pads during their periods, study finds
A third of teens and young adults in the U.S. can’t afford or otherwise access menstrual products, according to new research from Children’s National Hospital in Washington, D.C. The study found that “period poverty” — that is, insufficient access to menstrual hygiene products and related education — appears to affect young people equally, despite differences…
-
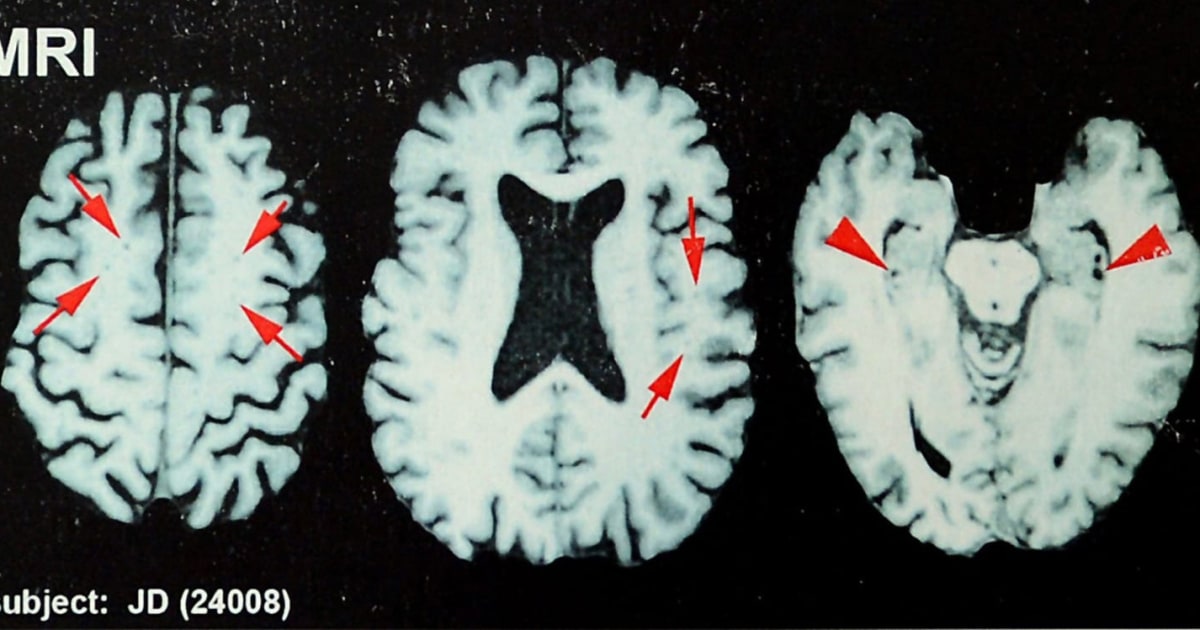
A third of former NFL players surveyed think they have CTE: study
The Summary Roughly one-third of former professional football players surveyed believe they have CTE, a study found. The brain disease — which is linked to repeated hits to the head — can only be officially diagnosed after death. But the new research indicates that many former NFL players have experienced symptoms associated with CTE, including…
-
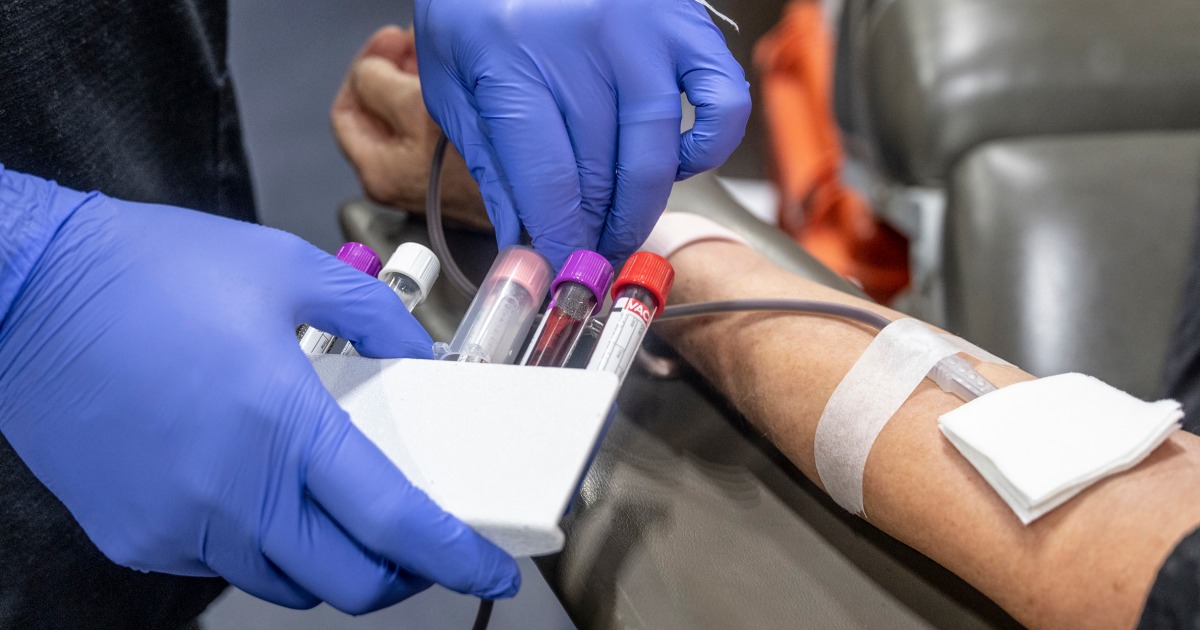
Iron deficiency may affect nearly 1 in 3 Americans, new study finds
Nearly 1 in 3 Americans may have an undiagnosed iron deficiency, a problem that can lead to fatigue, brain fog and difficulty concentrating, a new study suggests. An analysis of data from more than 8,000 adults in the U.S. revealed that 14% had low iron blood levels, a condition known as absolute iron deficiency, while…